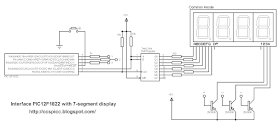
The easiest way to interface 7-segment display with PIC12F1822 microcontroller is to add a serial-in parallel-out shift register. The adding of the shift register
minimizes the number of pins used by the 7-segment display. This topic shows
how to make a 3-digit digital counter with multiplexing and 74HC164
shift register using PIC16F877A and CCS PIC C compiler.
Interfacing PIC12F1822 with 7-segment display circuit:Here is an example shows how to make a digital up counter where the number is displayed on a 7 segment display uses multiplexing technique with shift register.
Example circuit schematic is shown below where a common anode 7-segment display and 74HC164N shift register are used.
Other shift registers such as 74HC595 or CD4094 can be used in this project.
The displayed number can be incremented using the button which is connected to RA3 pin.
The push button is connected to RA3 pin. The shift register used is 74HC164 but other types can work properly like 74HC595 or CD4094.
In this example all pins of PIC12F1822 are used and there is no free pin.
Interfacing PIC12F1822 with 7-segment display CCS C code:
// Interfacing PIC12F1822 with 7-segment display
// Common anode 7-segment display used
// http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/
// electronnote@gmail.com
#include <12F1822.h>
#fuses NOMCLR INTRC_IO
#use delay(clock=8000000)
#use fast_io (a)
short s; // Used to know button position
unsigned int j, digit, digit1, digit10, digit100;
unsigned long i = 0;
unsigned int seg(unsigned int num) {
switch (num) {
case 0 : return 0xC0;
case 1 : return 0xF9;
case 2 : return 0xA4;
case 3 : return 0xB0;
case 4 : return 0x99;
case 5 : return 0x92;
case 6 : return 0x82;
case 7 : return 0xF8;
case 8 : return 0x80;
case 9 : return 0x90;
}
}
void main() {
setup_oscillator(OSC_8MHZ); // Set internal oscillator to 8MHz
set_tris_a(8); // Configure RA3 pin as input
port_a_pullups(8); // Enable RA3 internal pull-up
while(TRUE) {
if(input(PIN_A3) == 1)
s = 1;
if(s == 1) {
if(input(PIN_A3) == 0) {
s = 0;
i++;
if(i > 999)
i = 0;
}
}
digit = i % 10;
digit1 = seg(digit);
output_a(7); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if(digit1 & j)
output_high(PIN_A4);
else
output_low(PIN_A4);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_A5);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_A5);}
output_low(PIN_A0); // Turn on display for ones
delay_ms(1);
digit = (i / 10) % 10;
digit10 = seg(digit);
output_a(7); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if((digit10 & j) != 0)
output_high(PIN_A4);
else
output_low(PIN_A4);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_A5);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_A5);}
output_low(PIN_A1); // Turn on display for tens
delay_ms(1);
digit = (i / 100) % 10;
digit100 = seg(digit);
output_a(7); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if((digit100 & j) != 0)
output_high(PIN_A4);
else
output_low(PIN_A4);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_A5);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_A5);}
output_low(PIN_A2); // Turn on display for hundreds
delay_ms(1);
}
}
Interfacing PIC12F1822 with 7-segment display video:
The following video shows project in a hardware circuit with some details.