In this blog there are some topics shows how to control the bipolar stepper motor as the following one:
Bipolar stepper motor control with PIC16F877A microcontroller
Now in this topic an IR remote control is used to control the bipolar stepper motor speed and direction of rotation. The remote control used in this project uses NEC protocol and to see how to decode NEC protocol using PIC16F877A microcontroller see the following post:
NEC Protocol IR remote control decoder with PIC16F877A microcontroller
To control the bipolar stepper motor we need two H-bridge circuits and for that L293D motor driver chip is used, this cheap chip can work as a dual H-bridge drivers.
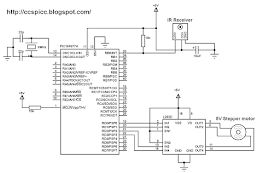
Project circuit schematic is shown below:
Remote controlled stepper motor using PIC16F877A CCS C code:
The IR remote control used in this project is shown below with the used buttons and their codes which are used in the code.
External interrupt is used for reading IR signals.
// Remote controlled bipolar stepper motor using PIC16F877A and L293D CCS C code // http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/ // electronnote@gmail.com #include <16F877A.h> #fuses HS,NOWDT,NOPROTECT,NOLVP #use delay(clock = 8000000) #use fast_io(B) #use fast_io(D) unsigned int8 step_number = 0, speed_delay = 2; unsigned int32 remote_code; #INT_TIMER1 // Timer1 interrupt ISR void timer1_isr(void){ remote_code = 0; clear_interrupt(INT_TIMER1); disable_interrupts(INT_TIMER1); } #INT_EXT // External interrupt ISR void ext_isr(void){ unsigned int8 count = 0, i; unsigned int32 ir_code; // Check 9ms pulse (remote control sends logic high) while((input(PIN_B0) == 0) && (count < 200)){ count++; delay_us(50);} if( (count > 199) || (count < 160)) // NEC protocol? return; count = 0; // Check 4.5ms space or repeated code while((input(PIN_B0)) && (count < 100)){ count++; delay_us(50);} if( (count > 99) || (count < 30)) // NEC protocol? return; // Check repeated code if(count < 60){ count = 0; while((input(PIN_B0) == 0) && (count < 14)){ count++; delay_us(50);} if( (count > 13) || (count < 8)) // NEC protocol? return; if((remote_code == 0x40BF50AF) || (remote_code == 0x40BF906F)) set_timer1(0); } // Read message (32 bits) for(i = 0; i < 32; i++){ count = 0; while((input(PIN_B0) == 0) && (count < 14)){ count++; delay_us(50);} if( (count > 13) || (count < 8)) // NEC protocol? return; count = 0; while((input(PIN_B0)) && (count < 40)){ count++; delay_us(50);} if( (count > 39) || (count < 8)) // NEC protocol? return; if( count > 20) // If space width > 1ms bit_set(ir_code, (31 - i)); // Write 1 to bit (31 - i) else // If space width < 1ms bit_clear(ir_code, (31 - i)); // Write 0 to bit (31 - i) } if((ir_code == 0x40BF50AF) || (ir_code == 0x40BF906F)){ set_timer1(0); clear_interrupt(INT_TIMER1); enable_interrupts(INT_TIMER1);} if(ir_code == 0x40BFA05F){ speed_delay++; if(speed_delay > 20) speed_delay = 20; return;} if(ir_code == 0x40BF609F){ speed_delay--; if(speed_delay < 2) speed_delay = 2; return;} remote_code = ir_code; } void stepper(int8 step){ switch(step){ case 0: output_d(0b000000110); break; case 1: output_d(0b00000101); break; case 2: output_d(0b00001001); break; case 3: output_d(0b00001010); break; } } void main(){ output_b(0); // PORTB initial state set_tris_b(0xF7); port_b_pullups(TRUE); // Enable PORTB internal pull-ups output_d(0); set_tris_d(0); setup_timer_1(T1_INTERNAL | T1_DIV_BY_4); // Timer1 configuration enable_interrupts(GLOBAL); // Enable global interrupts enable_interrupts(INT_EXT_H2L); // Enable external interrupt while(TRUE){ while(remote_code == 0); while((remote_code == 0x40BF40BF) || (remote_code == 0x40BF50AF)){ step_number++; if(step_number > 3) step_number = 0; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(speed_delay); } while((remote_code == 0x40BF807F) || (remote_code == 0x40BF906F)){ if(step_number < 1) step_number = 4; step_number--; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(speed_delay); } output_d(0); if((remote_code != 0x40BF40BF) && (remote_code != 0x40B807F)) remote_code = 0; } }
Remote controlled stepper motor using PIC16F877A video:
The following video shows a hardware circuit for this project.