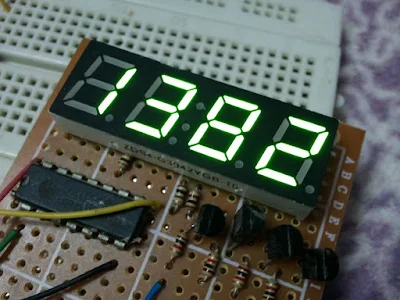
Digital up/down counter using PIC16F877A and CCS C
A
serial-in parallel-out shift register (74HC164, 74HC595, CD4094.....)
can be added to a 7-segment display. The adding of the shift register
minimizes the number of pins used by the 7-segment display. This topic shows
how to make a 4-digit digital counter with multiplexing and 74HC164
shift register using PIC16F877A and CCS PIC C compiler.Digital up/down counter using PIC16F877A:
Here is an example shows how to make a digital up and down counter where the number is displayed on a 7 segment display uses multiplexing technique with shift register.
Example circuit schematic is shown below where a common anode 7-segment display and 74HC164N shift register are used.
Other shift registers such as 74HC595 or CD4094 can be used in this project.
Two buttons are used to increment and decrement the displayed number.

Digital up/down counter using PIC16F877A CCS C code:
// 4-Digit digital counter using PIC16F877A
// Common anode 7-segment display with shift register
// http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/
// electronnote@gmail.com
#include <16F877A.h>
#use delay(crystal=8000000)
short s; // Used to know buttons position
unsigned int j, digit, digit1, digit10, digit100,digit1000;
unsigned long i = 0;
unsigned int seg(unsigned int num) {
switch (num) {
case 0 : return 0xC0;
case 1 : return 0xF9;
case 2 : return 0xA4;
case 3 : return 0xB0;
case 4 : return 0x99;
case 5 : return 0x92;
case 6 : return 0x82;
case 7 : return 0xF8;
case 8 : return 0x80;
case 9 : return 0x90;
}
}
void main(){
while(TRUE){
if(input(PIN_D0) && input(PIN_D1))
s = 1;
if(s == 1) {
if(input(PIN_D0) == 0) {
s = 0;
i++;
if(i > 9999)
i = 0;
}
if(input(PIN_D1) == 0) {
s = 0;
if(i < 1)
i = 1;
i--;
}
}
digit = i % 10;
digit1 = seg(digit);
output_c(0x0F); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if(digit1 & j)
output_high(PIN_B0);
else
output_low(PIN_B0);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_B1);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_B1);}
output_c(0x07); // Turn on display for ones
delay_ms(2);
digit = (i / 10) % 10;
digit10 = seg(digit);
output_c(0x0F); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if(digit10 & j)
output_high(PIN_B0);
else
output_low(PIN_B0);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_B1);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_B1);}
output_c(0x0B); // Turn on display for tens
delay_ms(2);
digit = (i / 100) % 10;
digit100 = seg(digit);
output_c(0x0F); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if(digit100 & j)
output_high(PIN_B0);
else
output_low(PIN_B0);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_B1);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_B1);}
output_c(0x0D); // Turn on display for hundreds
delay_ms(2);
digit = (i / 1000) % 10;
digit1000 = seg(digit);
output_c(0x0F); // Turn off all displays
for(j = 0x40; j > 0; j = j >> 1) {
if(digit1000 & j)
output_high(PIN_B0);
else
output_low(PIN_B0);
delay_us(10);
output_high(PIN_B1);
delay_us(10);
output_low(PIN_B1);}
output_c(0x0E); // Turn on display for thousands
delay_ms(2);
}
}
Digital up/down counter using PIC16F877A video:
The following video from a real hardware circuit for the digital counter.