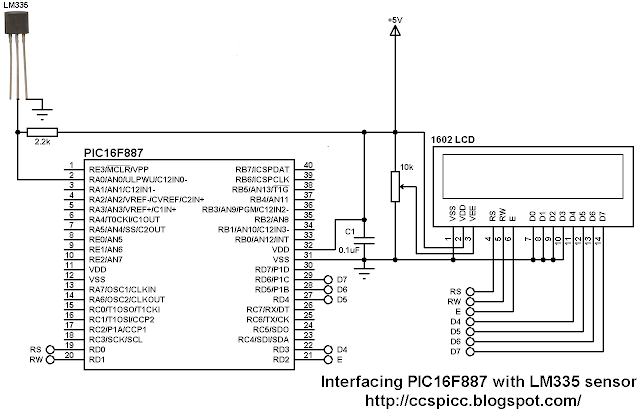
This is an example showing how to connect LM335 temperature sensing device with PIC16F887 microcontroller.
The LM335 is an analog device which requires an ADC module to convert the analog data which is the voltage output from the LM335 into digital data. The LM335 has the following features:
- Directly Calibrated to the Kelvin Temperature Scale
- 1°C Initial Accuracy Available
- Operates from 400 μA to 5 mA
- Less than 1-Ω Dynamic Impedance
- Easily Calibrated
- Wide Operating Temperature Range
- 200°C Overrange
- Low Cost
Hardware Required:
- PIC16F887 Microcontroller
- LM335 Temperature sensor
- 16x2 LCD Screen
- 10K ohm potentiometer or variable resistor
- 2.2K ohm resistor
- 0.1µF Ceramic capacitor (optional)
- +5V Power supply source
- Breadboard
- Jumper wires
This is our example circuit where the microcontroller uses its internal oscillator.
The LM335 has 3 pins:
Pin 1 for calibration, not used in this example
Pin 2: output
Pin 3: GND (ground)
Interfacing PIC16F887 with LM335 C code:
The C code used in this example is as the one below where it has been compiled with CCS PIC C compiler version 5.051.
/* Interfacing PIC16F887 with LM335 analog temperature sensor CCS C code Read LM335 datasheet to understand the code! Internal oscillator used @ 8MHz http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/ electronnote@gmail.com */ //LCD module connections #define LCD_RS_PIN PIN_D0 #define LCD_RW_PIN PIN_D1 #define LCD_ENABLE_PIN PIN_D2 #define LCD_DATA4 PIN_D3 #define LCD_DATA5 PIN_D4 #define LCD_DATA6 PIN_D5 #define LCD_DATA7 PIN_D6 //End LCD module connections #include <16F887.h> #fuses NOMCLR NOBROWNOUT NOLVP INTRC_IO #device ADC = 10 #use delay(clock = 8MHz) #include <lcd.c> char message1[] = "Temp = 00.0 C"; char message2[] = "= 00.0 K"; signed int16 Kelvin, Celsius; void main(){ setup_oscillator(OSC_8MHZ); // Set the internal oscillator to 8MHz setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_INTERNAL); // ADC Module uses its internal oscillator setup_adc_ports(sAN0); // Configure AN0 pin as analog set_adc_channel(0); // Select channel 0 (AN0) lcd_init(); // Initialize LCD module lcd_putc('\f'); // Clear LCD while(TRUE){ delay_ms(1000); Kelvin = read_adc() * 0.489; // Rea analog voltage and convert it to Kelvin (0.489 = 500/1023) Celsius = Kelvin - 273; // Convert Kelvin to degree Celsius if(Celsius < 0){ Celsius = abs(Celsius); // Absolute value message1[7] = '-'; // Put minus '-' sign } else message1[7] = ' '; // Put space ' ' if (Celsius > 99) message1[7] = 1 + 48; // Put 1 (of hundred) message1[8] = (Celsius / 10) % 10 + 48; message1[9] = Celsius % 10 + 48; message1[12] = 223; // Degree symbol message2[2] = (Kelvin / 100) % 10 + 48; message2[3] = (Kelvin / 10) % 10 + 48; message2[4] = Kelvin % 10 + 48; lcd_gotoxy(1, 1); // Go to column 1 row 1 printf(lcd_putc, message1); // Display message1 lcd_gotoxy(6, 2); // Go to column 6 row 2 printf(lcd_putc, message2); // Display message2 } }The following video shows Proteus simulation of LM335 and PIC16F887:
Proteus simulation file can be downloaded from this link:
PIC16F887 + LM335 - Proteus
Reference:
LM335 Datasheet