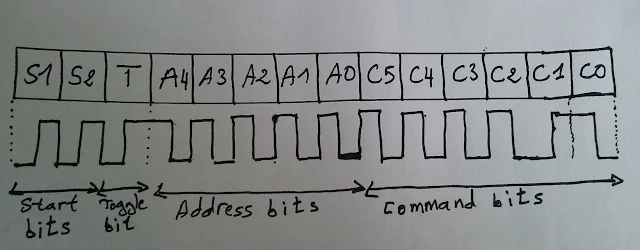
Low power DC motors can be easily controlled with half H-bridge IC L293D. This IC is 16-pin IC which can control 2 motors in both directions.
This topic shows how to control DC motor speed and direction with PIC16F84A and L293D motor drive integrated circuit.
Related topics:
The following topic shows how to control a DC motor with PIC16F84A and H-bridge circuit.
DC Motor speed and direction control with PIC16F84A using H-bridge
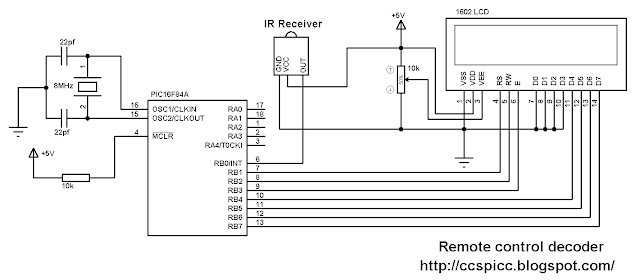
DC motor control with PIC16F84A and L293D circuit:
Project circuit schematic is shown below
The nominal voltage of the motor is 12V as well as L293D VS input voltage. Always L293D VS voltage is the same as the DC motor voltage and L293D VSS voltage is +5V.
In the circuit there are 5 buttons, the first button which is connected to RB0 pin is used to speed up the motor, and speed down button to decrease motor speed. Third and fourth buttons are used to choose direction rotation of the motor (direction 1 or direction 2). The last button stops the motor no matter what speed or direction.
There are 3 LEDs, LED1 and LED2 are used to indicate motor direction, and the other LED indicates maximum speed, which means when it is on the motor is running at maximum speed.
When speed up button is pressed the PWM duty cycle increases which causes the motor to increase its speed and when the duty cycle = 100 LED 3 turned on. In the other hand if speed down button is pressed the duty cycle decreases and the motor speed also decreases.
If the stop button pressed the motor stops and the 3 LEDs are off.
Software PWM is used wih frequency of 500Hz.
DC Motor control with PIC16F84A and L293D CCS C code:
The full C code is shown below. Official software PWM library which comes with CCS PIC C compiler is used, this library uses Timer0 to generate the PWM signal.
// DC motor control using PIC16F84A and L293D CCS C code
// http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/
// electronnote@gmail.com
#include <16F84A.h>
#fuses HS,NOWDT,PUT,NOPROTECT
#use delay(clock = 8000000)
#use fast_io(A)
#use fast_io(B)
#use pwm(output = pin_a0, output = pin_a1, timer = 0, frequency= 500Hz, duty = 0)
unsigned int8 i = 1;
void main() {
port_b_pullups(TRUE); // Enable PORTB pull-ups
output_a(0); // PORTA initial state
set_tris_a(0); // All PORTA pins are configured as outputs
output_b(0); // PORTB initial state
set_tris_b(0x1F); // Configure RB0 to RB4 as inputs
pwm_off(); // Turn off all pwm outputs
while(TRUE) {
if(input(PIN_B0) == 0){ // If RB0 button pressed
i++; // Increment i by 1 (i = i + 1)
if(i > 99){
i = 100;
output_high(PIN_B7);} // RB7 LED ON
pwm_set_duty_percent(i * 10UL); // Duty cycle change in tenths %
delay_ms(100); } // Wait 100ms
if(input(PIN_B1) == 0){ // If RB1 button pressed
output_low(PIN_B7); // RB7 LED OFF
i--; // Decrement i by 1 (i = i - 1)
if(i < 1)
i = 1;
pwm_set_duty_percent(i * 10UL); // Duty cycle change in tenths %
delay_ms(100); } // Wait 100ms
if(input(PIN_B2) == 0){ // If RB2 button pressed
if(input(PIN_B5) == 0){
output_low(PIN_B6); // RB6 LED OFF
pwm_off(); // Turn off pwm for both outputs
output_a(0); // PORTA pins low
delay_ms(100); // Wait 100ms
pwm_on(PIN_A0); // Turn pwm on at RA0
output_high(PIN_B5); // RB5 LED ON
if(i > 99)
output_high(PIN_B7);}}
if(input(PIN_B3) == 0){ // If RB3 button pressed
if(input(PIN_B6) == 0){
output_low(PIN_B5); // RB5 LED OFF
pwm_off(); // Turn off pwm for both outputs
output_a(0); // PORTA pins low
delay_ms(100); // Wait 100ms
pwm_on(PIN_A1); // Turn PWM on at RA1
output_high(PIN_B6);
if(i > 99)
output_high(PIN_B7);}}
if(input(PIN_B4) == 0){ // If RB4 button pressed
pwm_off(); // Turn off pwm for both outputs
output_a(0); // PORTA pins low
output_b(0);} // PORTB pins low
}
}
DC Motor control with PIC16F84A and L293D video:
The following video shows a hardware circuit of the project.