This topic shows how to drive 5V unipolar stepper motor in 3 modes one-phase, two-phase and half step. The microcontroller used in this project is Microchip PIC12F1822 and the motor drive circuit is ULN2003.
Usually the unipolar stepper motor has 5 wires one for motor supply and the other for coils. This motor has 4 coils and they are connected as shown in the figure below:
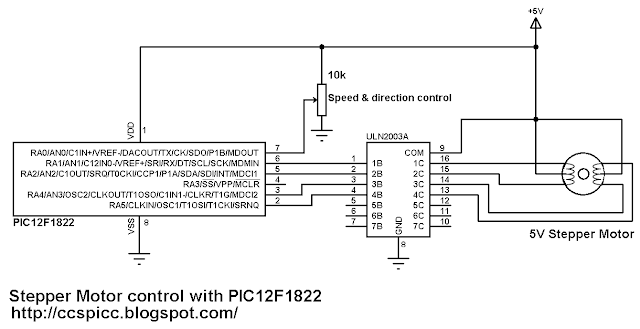
Unipolar Stepper Motor Control Example with PIC12F1822 circuit:
All the three control modes have the same circuit schematic as shown below.
Here PIC12F1822 uses its internal oscillator.
The potentiometer connected to AN0 is used to control motor speed and direction of rotation.
Unipolar Stepper Motor Control Example with PIC12F1822 CCS C code:
One Phase On Mode (Full Step mode):
In one phase control mode only one coil is energized at once. This mode produces smooth motion with low power consumption. Control sequence has 4 steps as shown in the table below:
CCS C code:
/* Unipolar stepper Motor control using PIC12F1822 (one-phase full step mode) CCS PIC C code http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/ electronnote@gmail.com */ #include <12F1822.h> #fuses NOMCLR INTRC_IO PLL_SW #device ADC = 8 // Set ADC resolution to 8-bit #use delay(clock=32000000) #use fast_io(A) unsigned int8 i, step_number = 0; void stepper(int8 step){ switch(step){ case 0: output_a(0b100000); break; case 1: output_a(0b010000); break; case 2: output_a(0b000100); break; case 3: output_a(0b000010); break; } } void main() { setup_oscillator(OSC_8MHZ | OSC_PLL_ON); // Set internal oscillator to 32MHz (8MHz and PLL) output_a(0); set_tris_a(1); // Configure RA0 pin as input setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_DIV_32); // Set ADC conversion time to 32Tosc setup_adc_ports(sAN0); // Configure AN0 pin as analog set_adc_channel(0); // Select channel AN0 while(TRUE){ output_a(0); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i while(i >= 128){ // Move motor in direction 1 step_number++; if(step_number > 3) step_number = 0; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(257 - i); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } while(i < 128){ // Move motor in direction 2 if(step_number < 1) step_number = 4; step_number--; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(i + 2); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } } }Two Phases On Mode (Alternate Full Step mode):
In two-phase mode two coils are energized. This mode produces high torque but its motion is not smooth like the one phase mode. The following table shows this mode sequence:
CCS C code:
/* Unipolar stepper Motor control using PIC12F1822 (two-phase full step mode) CCS PIC C code http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/ electronnote@gmail.com */ #include <12F1822.h> #fuses NOMCLR INTRC_IO PLL_SW #device ADC = 8 // Set ADC resolution to 8-bit #use delay(clock=32000000) #use fast_io(A) unsigned int8 i, step_number = 0; void stepper(int8 step){ switch(step){ case 0: output_a(0b100010); break; case 1: output_a(0b110000); break; case 2: output_a(0b010100); break; case 3: output_a(0b000110); break; } } void main() { setup_oscillator(OSC_8MHZ | OSC_PLL_ON); // Set internal oscillator to 32MHz (8MHz and PLL) output_a(0); set_tris_a(1); // Configure RA0 pin as input setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_DIV_32); // Set ADC conversion time to 32Tosc setup_adc_ports(sAN0); // Configure AN0 pin as analog set_adc_channel(0); // Select channel AN0 while(TRUE){ output_a(0); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i while(i >= 128){ // Move motor in direction 1 step_number++; if(step_number > 3) step_number = 0; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(257 - i); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } while(i < 128){ // Move motor in direction 2 if(step_number < 1) step_number = 4; step_number--; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(i + 2); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } } }Half Step Mode:
This mode is just mix of the previous two mode sequences. The half step mode increases motor number of steps by 2, for example a stepper motor of 24 steps of 15 degrees each, it becomes using half step mode 28 steps of 7.5 degrees. Mode sequence shown below:
CCS C code:
/* Unipolar stepper Motor control using PIC12F1822 (half step mode) CCS PIC C code http://ccspicc.blogspot.com/ electronnote@gmail.com */ #include <12F1822.h> #fuses NOMCLR INTRC_IO PLL_SW #device ADC = 8 // Set ADC resolution to 8-bit #use delay(clock=32000000) #use fast_io(A) unsigned int8 i, step_number = 0; void stepper(int8 step){ switch(step){ case 0: output_a(0b100010); break; case 1: output_a(0b100000); break; case 2: output_a(0b110000); break; case 3: output_a(0b010000); break; case 4: output_a(0b010100); break; case 5: output_a(0b000100); break; case 6: output_a(0b000110); break; case 7: output_a(0b000010); break; } } void main() { setup_oscillator(OSC_8MHZ | OSC_PLL_ON); // Set internal oscillator to 32MHz (8MHz and PLL) output_a(0); set_tris_a(1); // Configure RA0 pin as input setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_DIV_32); // Set ADC conversion time to 32Tosc setup_adc_ports(sAN0); // Configure AN0 pin as analog set_adc_channel(0); // Select channel AN0 while(TRUE){ output_a(0); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i while(i >= 128){ // Move motor in direction 1 step_number++; if(step_number > 7) step_number = 0; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(257 - i); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } while(i < 128){ // Move motor in direction 2 if(step_number < 1) step_number = 8; step_number--; stepper(step_number); delay_ms(i + 2); i = read_adc(); // Read from AN0 and store in i } } }Example Video: